Traitements d'identités numériques
Fiabilisation, recherche et appariements jusqu'à 100 millions d'identités
Traitements d'identités numériques
Fiabilisation, recherche et appariements jusqu'à 100 millions d'identités
make up do?make up may take some time, because it handles multiple actions :
node,nginx,python,elasticsearch,kibana)Vue.js frontend with node into static html/css/js filespython backend, with all pandas and scikit-learn dependenciespython backendelasticsearch cluster (if you need less, just edit Makefile and set ES_NODE to 1)kibana (required for launching it for now)nginx for serving stating compile frontend, and reverse proxy of the backend, elasticsearch and kibanaHere is the architecture overview :
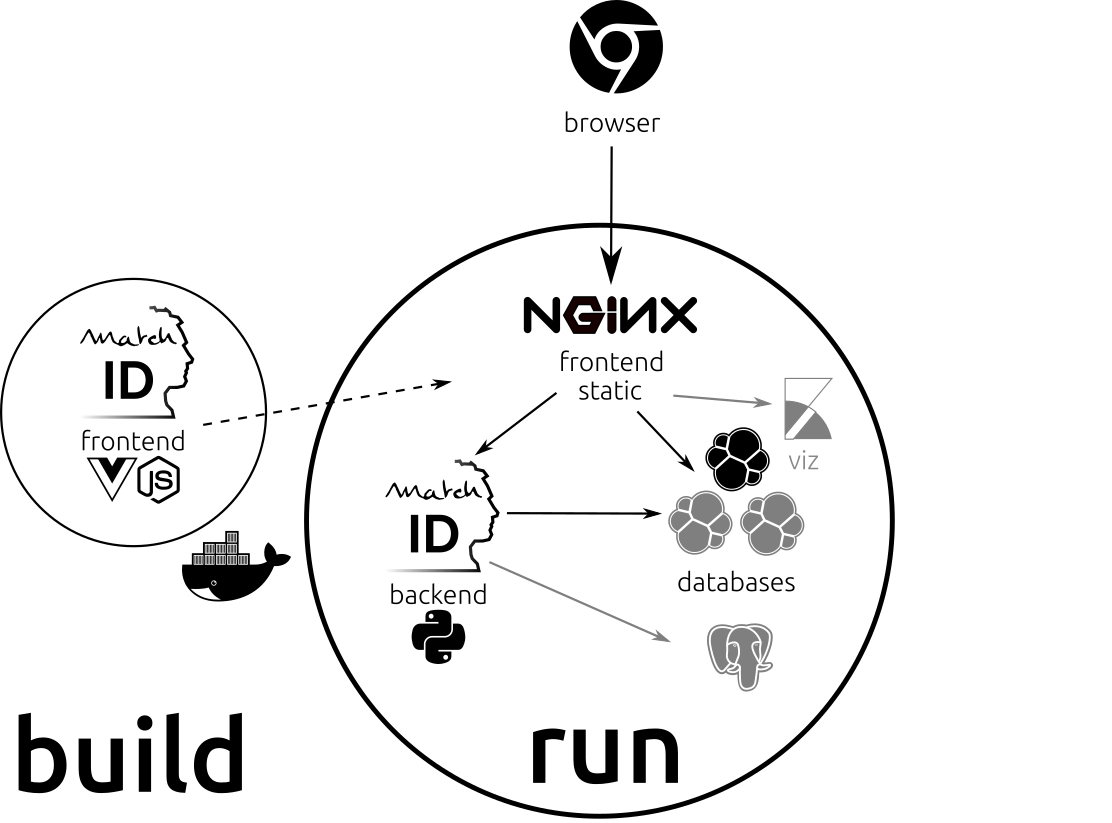
All commands here have to be executed from the machine where docker runs matchID (local or remote).
To stop all components
make stop
make backend-stopmake backendmake backend-stop backenddocker logs -f matchid-backendmake docker-buildmake frontend-stopmake frontendmake frontend-stop frontenddocker logs -f matchid-backendElasticsearch is useful for powerfull fuzzy matching with levenshtein distance (but could be replaced with a phonetic or ngram indexation with postgres) and is required for now by the validation module.
make elasticsearch-stopmake elasticsearchmake elasticsearch-stop elasticsearchdocker ps | egrep 'matchid-(elasticsearch|esnode)', you should have a line for every containerdocker logs -f matchid-elasticsearch, you may replace elasticsearch with esnode2, esnode3, depending of the number of nodes you haveSee avanced elasticsearch troubleshooting for configuring your cluster and more about elasticsearch and docker.
Postgres is not mandatory, so it is not up when you start. Postgres can be useful for a more reliable storage than elasticsearch, or to replace elasticsearch for quicker ngram matching.
make postgresmake postgres-stopmake postgres-stop postgresKibana has to be started on start (for a dependency of the nginx configuration). It can be useful to analyse your elasticsearch data, but is absolutely not mandatory (it will next not be a requirement).
make kibana-stopmake kibanamake kibana-stop kibanaSome useful commands :
docker stats shows all containers running, like a topYou can switch to developpement mode without stopping the whole sevices : make frontend-stop frontend-dev
Please consult contributing to developement.
When your run make start or make elasticsearch, the configuration of elasticsearch is created in docker-components/docker-compose-elasticsearch-huge.yml with one master and ES_NODES-1 nodes.
To change the configuration :
ES_NODES (default to 3, tested up to 20).ES_MEM (java memory).We’ve encountered stability problems with elasticsearch, docker and memory limitation (mem_limit). Elasticsearch recommends twice the memory of the jvm for the virtual machine memory. But setting hard memory limit with mem_limit seems to be a wrong with the docker virtualisation. So we supressed this limiation, which may lead to performance problem when strong sollicitation. This problem will be followed in the matchID project, as elasticsearch is an essential component.
to be completed
docker exec -it matchid-elasticsearch curl -XGET localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty, the status should be green and number_of_nodes to the ES_NODES value (default : 3)docker exec -it matchid-elasticsearch curl -XGET localhost:9200/_cat/indices, each indice should be green.Note that the API point of elasticsearch is accessible from any client (unless you protect this API with the nginx configuration) : http://${matchID-host}/matchID/elastiscearch is the same as localhost:9200/ within docker. For example, if you run matchID on your host :
curl -XGET http://localhost/matchID/elasticsearch/_cluster/health?prettycurl -XGET http://localhost/matchID/elasticsearch/_cat/indicesIf you have large indices and multiples nodes, the coherence of your cluster may take some time when you just started the cluster. You can then check the health indices.
If your cluster is red for some time (more than one minute) you should make elasticsearch restart.
If it is still red, check the docker logs -f of each node.
Many problems can occure :
curl -XDELETE http://localhost/matchID/elasticsearch/* and lose all indexed dataIt may be that one or many indices are red or at least one yellow. It may take some time but usually, elasticsearch self repairs.
With a persistent yellow state of an indice and the right amount of documents, you will still be able to access your data so that you may backup. You should do that with a recipe doing nothing from the dataset of your index to a msgpack dataset. Then try to restore it on another index, then delete the index.
You may have to delete every red and yellow indices.
Fabien est ingénieur et travaillait au sein de ministères régaliens sur la data et l'IA. Concepteur de matchID et de deces.matchid.io, il développe toujours avec plaisir les algorithmes aussi bien que les UI, sur son temps libre. Il a quitté depuis peu l'administration française, et reste passionné par les projets d'intérêt général.
Cristian est phD passionné de développement et technologie, expert en deeplearning. Il travaille aujourd'hui au ministère de l'Intérieur, où il a créé IA Flash, et contribue activement à matchID avec la création de l'API décès.
Martin est ingénieur et cofondateur de CommoPrices.com, la plus grosse plateforme de prix de matières premières he world biggest portal of commodity prices. Il a développé l'interface de validation de matchID pendant son challenge EIG.